The Golden Ratio In Art Explained With Examples
The golden ratio in art, often called nature’s perfect proportion, has fascinated painters, architects, and artists for centuries. This mathematical principle, represented by the number 1.618, is believed to create harmony and balance in visual compositions.
Artists and designers have used it to craft some of the most iconic and aesthetically pleasing works of art, from ancient architecture to modern designs.
In this exploration, we’ll understand the significance of the golden ratio in art, showcasing examples highlighting how this timeless concept continues to influence creativity and design.
Table Of Contents
What Is The Golden Ratio?
The golden ratio creates proportions that look balanced and natural. It’s a special number, approximately 1.618, that emerges when you divide a line into two parts so that the ratio of the longer part to the shorter part equals the ratio of the whole length to the longer part.
Here is the formula used to calculate that value:
This ratio appears in nature, art, and even our bodies; it’s far from a random number.
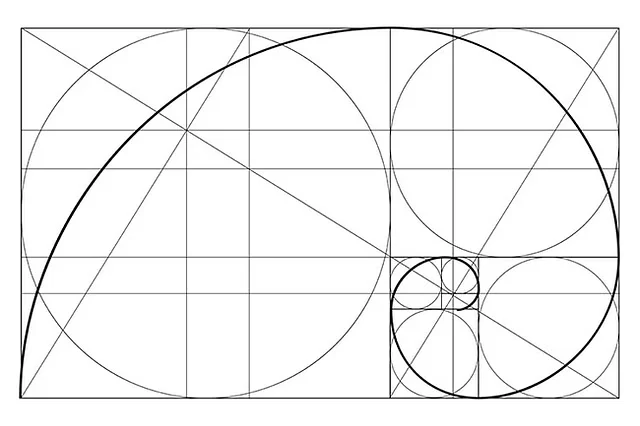
We often visualize the golden ratio through a spiral drawn by connecting the opposite corners of squares within a series of rectangles that follow this ratio.
The Golden Ratio In Art
The Golden Ratio has been a guiding principle in art for centuries, influencing the composition and structure of countless masterpieces. But what periods are we talking about? Let’s take a look.
Historical Periods Where the Golden Ratio Was Prominent in Art
Here are the periods where artwork featuring the golden ratio appeared:
- Ancient Greece and Rome
- Medieval Period
- Renaissance
- Baroque Period
- Modern Art (20th Century and Beyond)
The golden ratio originated in ancient Greece and Rome. Where architects and artists used it to design temples, sculptures, and other masterpieces. During the Renaissance, it became a central element in the works of artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo.
The golden ratio continues to inspire in modern times. Artists and designers of the 20th century, like Salvador Dali, embraced this mathematical principle. They created works that resonate deeply with viewers on a subconscious level.
Also, check out The Influence of Art History on Modern Pop Art – A Deep Dive.
Examples Of The Golden Ratio In Different Art
Now, let’s look at some examples of artworks with golden ratio applied. We’ll look at 7 of the most impressive and recognizable works.
1. The Taj Mahal In India
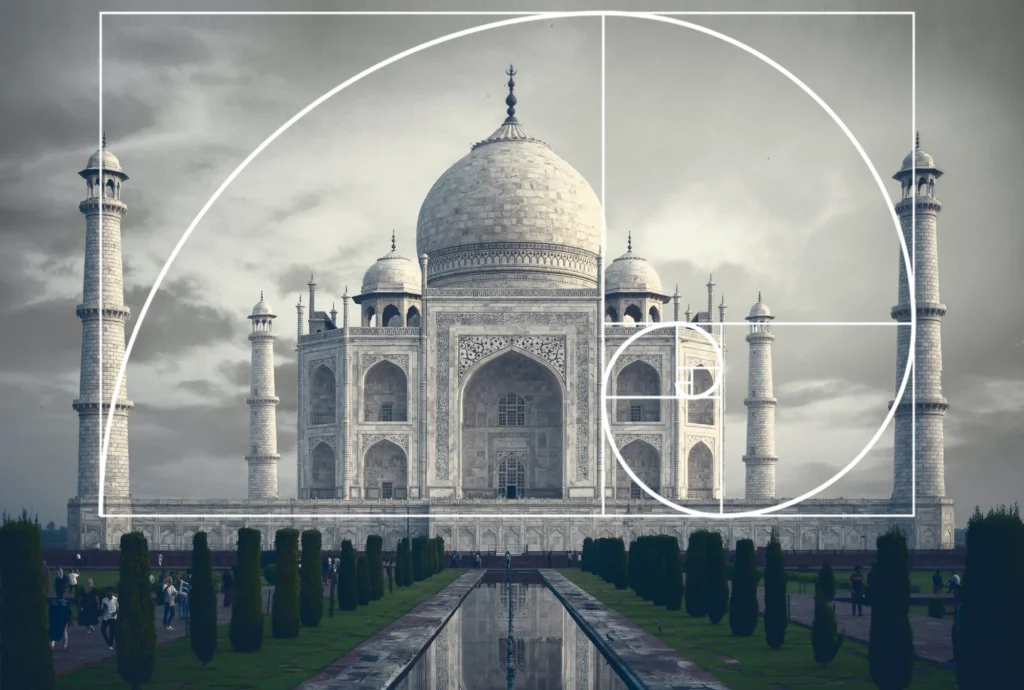

One of the best examples of the golden ratio in architecture is The Taj Mahal. Its symmetrical architecture incorporates the golden ratio in its design, particularly in the dimensions of the central dome and its surrounding elements. It creates a harmonious and visually pleasing structure.
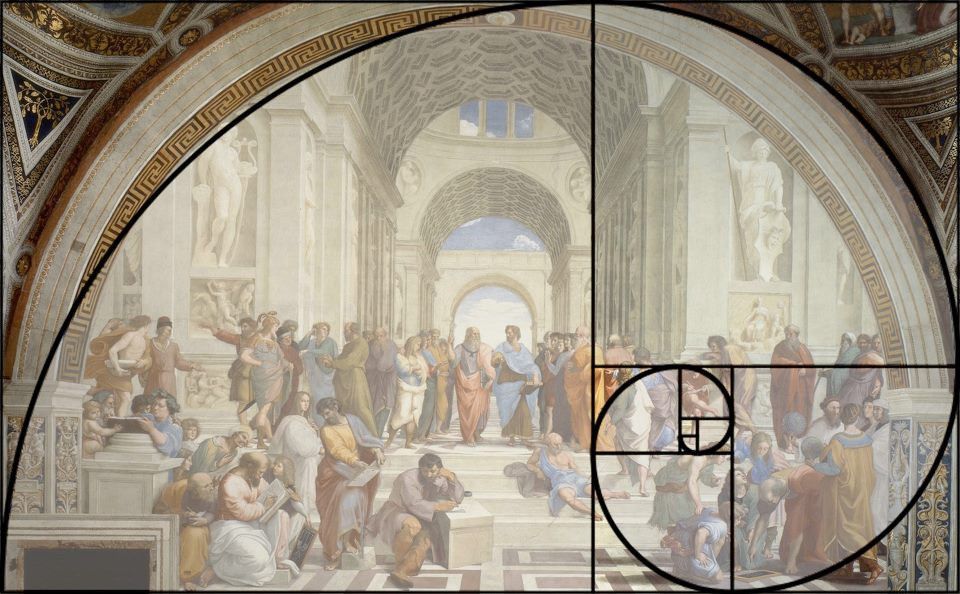
2. Raphael’s “The School of Athens”
Raphael used the Golden Ratio in “The School of Athens” to organize the composition, particularly in placing key figures like Plato and Aristotle, which enhances the balance and visual appeal of this iconic fresco.
Also, check out 9 Famous Portrait Paintings People Recreated Through Photos
3. Johannes Vermeer’s “Girl with a Pearl Earring”
Vermeer applied the Golden Ratio in the composition of “Girl with a Pearl Earring,” particularly in positioning the subject’s face and placing key elements, creating a balanced and captivating portrait.
Also, check out Design Inspiration From 15 Remakes of Famous Paintings
4. The Parthenon In Athens
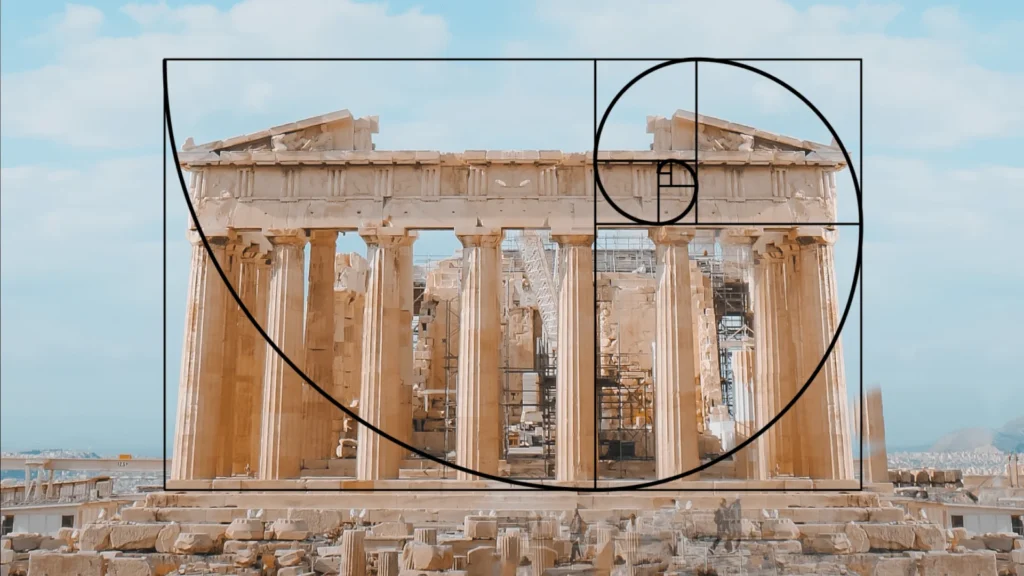

The Parthenon’s facade and proportions are designed according to the Golden Ratio, embodying the Greek pursuit of architectural perfection.
Also, check out Early Drawings of Famous Architects
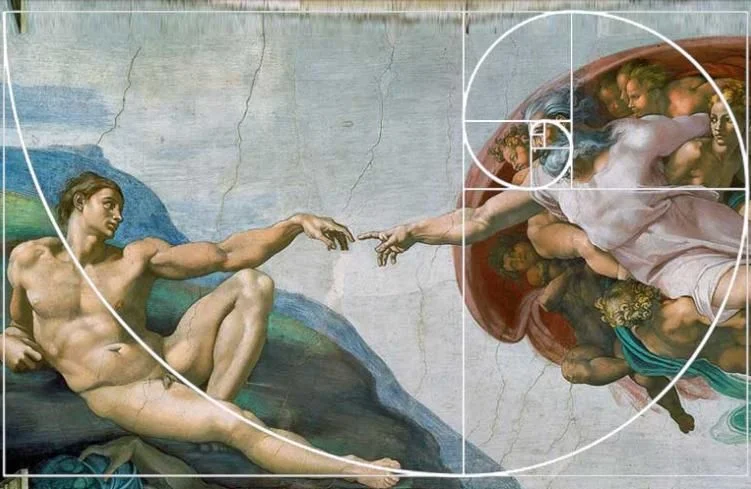
5. Michelangelo’s “Creation of Adam”
Michelangelo subtly incorporated the Golden Ratio in the composition, particularly in positioning Adam and God’s outstretched hands.
Also, check out Famous Art Used In Advertising: 15 Painting Ads Examples
6. Katsushika Hokusai’s “The Great Wave off Kanagawa”
Yet another example of the golden ratio in famous paintings. Hokusai’s “The Great Wave” subtly employs the Golden Ratio in the composition of the towering wave, guiding the viewer’s eye naturally through the scene, enhancing the balance between the wave, Mount Fuji, and the surrounding space.
Also, check out the 5700 Mega Design Elements Bundle
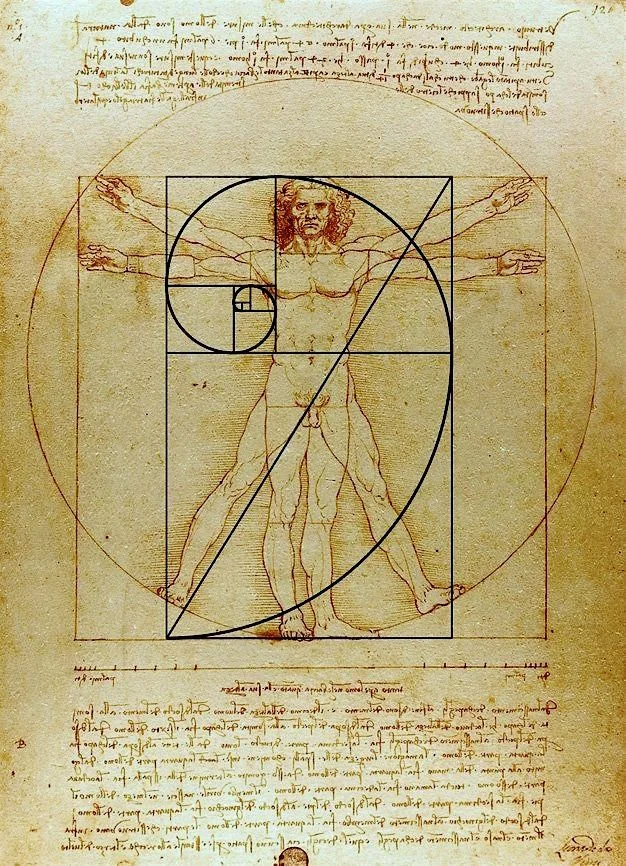
7. Leonardo Da Vinci’s “Vitruvian Man”
Number one, we have likely the most famous artwork, which includes the golden ratio, Leonardo’s “Vitruvian Man”. This illustration displays the perfection of human proportions, merging art, science, and mathematics into one.
Also, check out Modern Aztec Art and Culture | Interesting Historical Facts
Conclusion
The golden ratio is a timeless concept that has shaped art for millennia, making it more than just a mathematical marvel. Artists across eras, starting with the ancient Greeks, have used this ratio as a secret tool to achieve harmony and beauty in their visual compositions.
The grandeur of the Parthenon and the intricate details of Vermeer’s portraits are just two examples of how the golden ratio continues to captivate and inspire. As we’ve seen, this ratio isn’t just about numbers; it’s about creating a deep connection with the human eye through balance and beauty.
The next time you admire a work of art, consider the hidden harmony that might be at play.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the Mona Lisa use the golden ratio?
The Mona Lisa’s composition uses the golden ratio in the face’s proportions, enhancing balance and visual appeal, making the artwork pleasing to the human eye.
Did Da Vinci use the golden ratio?
Leonardo da Vinci frequently used the golden ratio, notably in works like “Vitruvian Man” and “Mona Lisa,” to achieve balance and harmony in his compositions.
What famous art uses the golden ratio?
Famous artworks using the golden ratio include Da Vinci’s “Vitruvian Man,” Michelangelo’s “Creation of Adam,” Vermeer’s “Girl with a Pearl Earring,” and the Parthenon in Athens. If you want to see how is the golden ratio used in art, these are great examples.
What is the golden ratio in simple terms?
The golden ratio is a mathematical proportion, approximately 1.618, that creates visually pleasing and balanced compositions. It is often found in nature, art, and architecture.
Like this post? Check out more amazing content on design history and art on our blog.
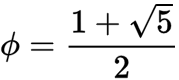




In my opinion, the golden ratio is not just a mathematical concept, but a powerful design principle that helps us create harmony and balance in works of art. It is fascinating to know that the golden ratio is just like basket random, both are great.
This sounds absolutely fascinating! I’m really intrigued by how the golden ratio, that 1.618 number, is believed to create harmony in art. I’m especially looking forward to seeing the examples that span from ancient architecture to modern designs. Great intro!
This is very informative and helpful for us.